Welding cobots, a term derived from ‘collaborative robots,’ are
an
innovative solution for robotic welding. Unlike thesetraditional welding
robots, cobots are designed to work alongside humans in a shared workspace.
They are engineered with sophisticated sensors and control systems, allowing
safe, efficient interaction with human operators. In today’s world
skilled
welders are hard to find, so an increasing number of companies use welding
cobots to automate the welding processes including high-mix, low-volume part
runs. This strategy then frees up skilled welders to tackle more complex
welding projects. And, as production levels grow, companies that have tried
cobot welders often look to traditional high-speed robotic welders to take
on low-mix, high-volume production.
Evolution of Robotic Welding
Robotic welding originated in the 1980s, marking a significant leap in
manufacturing technology. Due to their high-speed operations and lack of
sensing capabilities, traditional robotic systems are caged off from human
workers to prevent accidents. Over the decades, advancements in sensor
technology and artificial intelligence have paved the way for the emergence
of welding cobots. These modern marvels encapsulate the essence of
human-robot collaboration and make a great choice for small- to medium-sized
companies that are new to automation.
Differences Between Traditional Robots and Cobots
Traditional welding robots and cobots differ fundamentally in their
operation and interaction with human workers. Traditional robots operate
autonomously within caged areas, requiring a clear separation from human
activities to ensure safety. On the other hand, cobots are designed to share
the workspace with humans, with safety features that allow for close
interaction. The intuitive control systems of cobots enable easy programming
and operation, making them extremely easy to program and use. In addition,
cobots are compact and provide the flexibility and scalability to handle new
tasks in a matter of minutes.
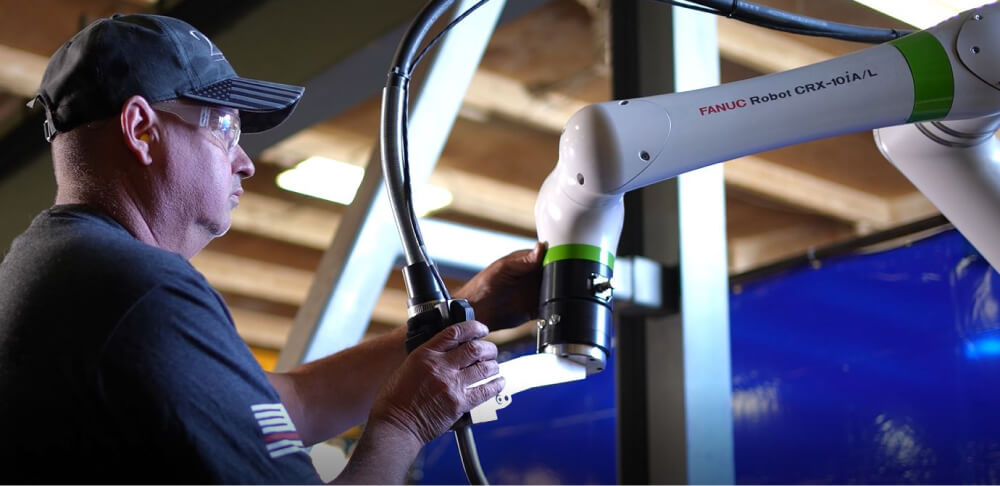

The Welder Shortage Crisis
Understanding the Crisis
The manufacturing sector is experiencing a significant shortage of skilled
welders. A combination of factors contributes to this crisis. Firstly, a
generation of skilled welders is approaching retirement, and there aren't
enough trained individuals to fill the gap. Secondly, despite its critical
role in manufacturing, welding often gets overlooked as a viable career by
the younger generation. The perception of welding as a dirty, dangerous, and
demanding job has deterred many from pursuing a career in this field.
Lastly, the rapid advancements in manufacturing technology require higher
skill and training, further widening the gap between available jobs and
qualified welders.
The Role of Cobot Welding in Addressing the Shortage
Cobot welding emerges as a promising solution to mitigate the welder
shortage crisis. Cobots allow human welders to focus on more complex and
critical aspects of the welding process by taking on repetitive, strenuous,
and precision-demanding tasks. Cobots come with user-friendly interfaces,
allowing for quick learning and easy operation, thus reducing the barrier to
entry for new welders. Moreover, the collaborative nature of cobots creates
a more engaging and safer work environment, potentially attracting a younger
workforce to the welding profession.
Cobot welding also allows for a scalable solution to varying production
demands. Companies can deploy cobots to maintain a steady production pace,
even in the face of fluctuating workforce availability. The integration of
cobots can help businesses keep up with technological advancements in the
welding industry, ensuring they remain competitive.
The deployment of welding cobots not only addresses the immediate issue of
welder shortage but also sets a foundation for a more sustainable and
technologically advanced welding industry. By augmenting human capabilities
with cobots, companies are better positioned to solve current and future
challenges in welding operations.
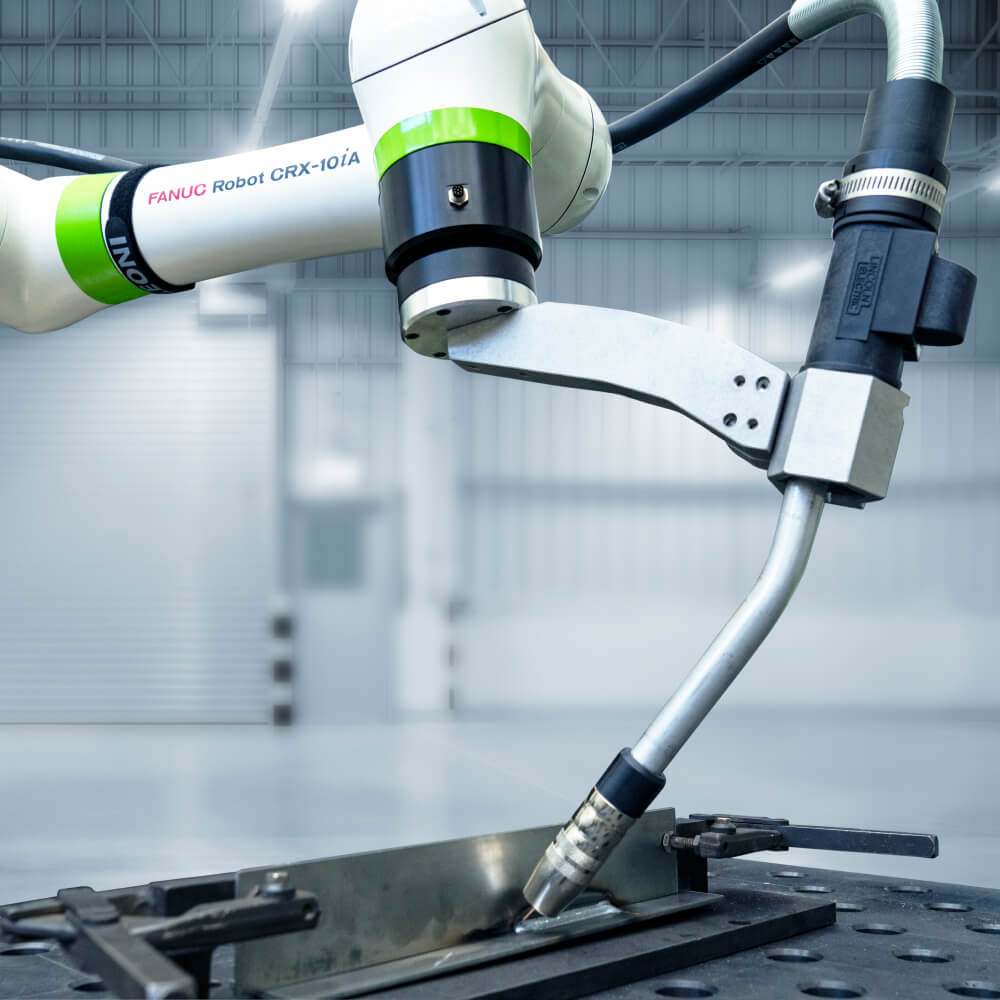

Benefits of Using Welding Cobots
Enhanced Precision and Consistency
Welding cobots, with their sophisticated control systems and steady robotic
arms, significantly enhance the precision and consistency of welding
operations. The meticulous control over welding parameters such as speed,
angle, and distance ensures that every weld is performed to the exact
specifications, reducing the margin of error that may be encountered in
manual welding. This level of precision is crucial, especially in industries
like aerospace or automotive manufacturing, where the quality of welds is
paramount.
Unlike human operators, cobots are immune to fatigue, ensuring consistent
weld quality 24 hours a day. This consistency translates to fewer defects,
lower rework costs, and higher product quality. The precision and
consistency provided by welding cobots is hard to match, making them an
indispensable asset in modern welding operaitons.
Increased Safety in Work Environments
Safety is paramount in welding or any manufacturing operations. Welding
cobots are designed with several built-in safety features that significantly
mitigate workplace risks. These features include force-limited joints,
real-time monitoring systems, and immediate cessation of operations if a
human enters a predefined proximity. Such safety measures minimize the
chances of accidents and collisions, ensuring a safer work environment.
By handling hazardous tasks such as operating in high-heat zones or dealing
with toxic materials, cobots drastically reduce the exposure of human
workers to potential health hazards associated with welding. A safer
workplace not only protects workers, it may encourage more
people to become welders. Integrating cobots into welding operations
symbolizes a significant step towards creating a safer, more controlled work
environment, showcasing the profound impact of collaborative robotics in
industrial safety protocols.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Welding cobots plays a big role in boosting welding efficiency and
productivity. With their tireless work ethic, cobots enable round-the-clock
operations, which are crucial in meeting tight production schedules and
deadlines. Their swift setup and ease of reconfiguration facilitate a faster
transition between different welding tasks, significantly reducing downtime
often associated with manual retooling.
The ability of cobots to handle repetitive and mundane tasks with a high
degree of speed and accuracy leads to increased throughput and better
resource utilization. The seamless execution of welding cobots results in
higher productivity rates, lower operating costs and optimized workflows,
enabling companies to maximize efficiencies and profits.
Flexibility and Ease of Deployment
One of the defining traits of welding cobots is their flexibility and ease
of deployment. Unlike traditional robots, cobots do not require extensive
setup or specialized facilities. Their compact design, user-friendly
interface, and easy programming make them highly adaptable to various
welding tasks and operational environments. This swift deployment and
redeployment across different tasks or locations are particularly beneficial
for small to medium-sized enterprises that may not have the resources for a
large-scale robotic system, but looking to automate one or more welding
processes.
The versatility of cobots allows companies to quickly adjust to new project
requirements. This flexibility fosters a more agile manufacturing
environment to meet the diverse and evolving demands of today’s
industrial
landscape. Through their easy integration and adaptable nature, welding
cobots help bridge the gap between automation and human-centric operations.
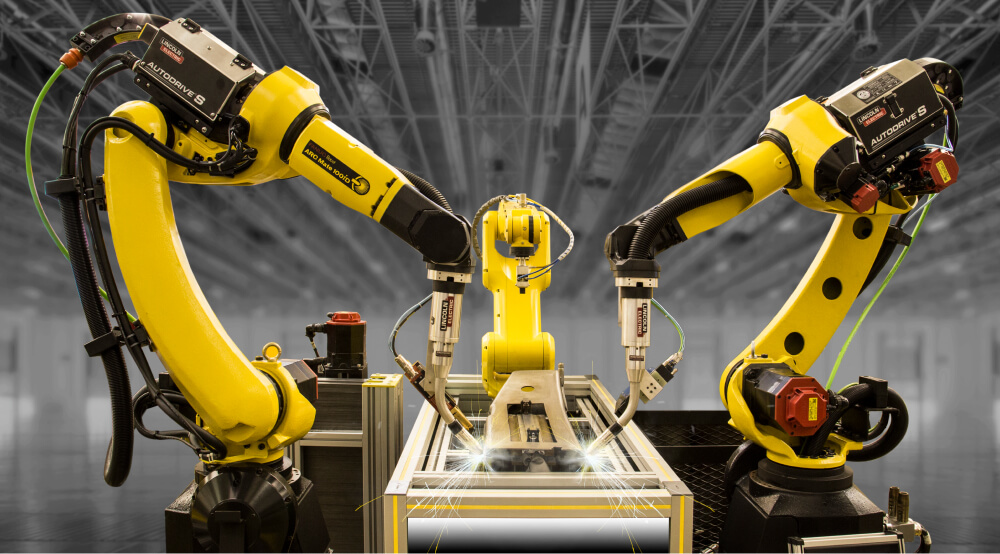

Technical Aspects of Welding Cobots
Key Components and Their Functions
Robotic Arm
The robotic arm is essentially the backbone of the welding cobot. It is
meticulously engineered to provide the movement, reach, and flexibility
required to perform welding tasks across various workpieces. The precision
in movement ensures that the welding torch is accurately positioned,
significantly impacting weld quality. Moreover, the robotic arm's speed and
accuracy play a pivotal role in enhancing welding efficiency and
productivity.
Welding Power Source
The welding power source is the heart of the welding operation. It supplies
the required energy to create stable, high-quality welds. The compatibility
between the power source and the welding cobot is crucial as it directly
influences the performance and the outcome of the welding tasks. It's
essential to match the power source to the welding cobot and the task at
hand to ensure optimal performance, making the selection of an appropriate
power source a critical consideration.
Torch
The welding torch directs the welding arc to the precise location on the
workpiece to ensure accurate, high-quality welds. The design and maintenance
of the torch are crucial as it interacts directly with the workpiece, and
any misalignment or malfunction could result in subpar welds.
Teaching Device
A teaching device, which could be a pendant or tablet, allows users to
program a cobot to perform welding tasks. An intuitive interface makes it
quick and easy to setup the welding path and parameters.
Welding Software
Welding software is the cornerstone of intelligent cobot welding. It adjusts
the welding program to maintain weld quality, especially when dealing with
inconsistent production parts. Advanced software options like Touch Sensing,
Arc Seam Tracking, and laser vision enhance the cobot's adaptability by
adding seam finding, seam tracking, or joint measurement capabilities. These
features are instrumental in ensuring that the cobot can effectively handle
various welding tasks with different workpiece geometries and conditions.
Pre-built Welding Libraries
Most manufacturers equip their cobots with pre-built welding libraries that
simplify the application of cobots to welding tasks. Functions like tool-tip
alignment and wire feed rate optimization are part of these libraries. They
enable easy adaptation to specific welding requirements, making the
transition to cobot welding much smoother for both small and large
companies.
Cable Feed Equipment
Although cobots generally have a lower payload capacity than traditional
robots, the design accommodates the cable feed equipment to be located off
the robot. This arrangement facilitates the setup and operation of the cobot
welding system, ensuring that its lower payload capacity does not impede its
functionality in the welding process.
Welding Techniques and Applications
Welding cobots support various welding techniques, including Arc welding,
MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), laser, plasma, ultrasonic,
and spot welding. Cobots can also be configured for soldering or brazing if
needed. This adaptability is notable in industries requiring different
welding techniques for varied materials and products.
With cobots, fabricators can create specific weld programs for individual
workpieces or parts, quickly switch between different weld programs and
workpieces, and establish a consistent, repeatable, semi-autonomous weld
workflow for increased productivity. This level of automation enables taking
on more orders without the need for additional welders, thus improving the
pricing, quoting process, and overall throughput.
The ability to automate almost any type of weld, including the commonly
automated MIG welds in thicker metal applications like aluminum, stainless
steel, and carbon steel, underscores the cobots’ extensive application
in
welding tasks. Cobots can also be integrated with Gas Metal Arc Welding
(GMAW) and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) processes, although using cobots
for different passes in these processes is less common. With their ease of
programming and adaptability, welding cobots are revolutionizing welding
applications across diverse sectors.
Programming and Automation
Programming welding cobots is streamlined to accommodate both seasoned
programmers and those with limited programming experience. A notable feature
of cobot welding systems is the reduced programming time facilitated by
user-friendly software solutions.
For instance, FANUC’s ARC Tool Software comes with an easy-to-program
interface that not only supports simple applications but also provides the
ability to utilize advanced features such as Weaving and iRVision, thereby
reducing the programming time and improving the bottom line for businesses.
The ease of programming extends to developing specific weld programs for
individual workpieces or parts and the ability to quickly switch between
different weld programs and workpieces as required swiftly. This level of
automation establishes a consistent, repeatable, and semi-autonomous weld
workflow, significantly enhancing productivity. It also allows for the
storage of weld programs for future reference, ensuring a quicker setup for
recurring welding tasks and thereby increasing the throughput of each shift.
Automation with cobots allows for a continual welding process as workers can
safely load and unload parts while the cobot welds, ensuring the system runs
continually for maximum productivity. This blend of automation and human
interaction paves the way for a more efficient welding workflow, opening new
avenues for scaling production and improving operational efficiencies.
Integration with Other Systems
Welding cobots are designed with integration in mind, allowing them to work
seamlessly alongside existing systems and processes in a manufacturing
setup. Industrial end users have been the driving force behind the
integration of welding systems and cobots. Companies like FANUC provide
welding cobots that work closely with your welding processes, showcasing the
industry's advanced cobot technology.
Integrating a welding cobot into an existing welding cell or other
manufacturing systems involves reconfiguring the application space. This
could mean utilizing a closed shop or opening it up to allow welders to move
around. System integration firms help manufacturing companies
design and commission industrial robots and other advanced automation
systems, with some able to install cobots for welding applications in a
matter of hours or days instead of weeks or months.
Integration specialists can help outfit the ideal setup, ensuring the
welding cobot and the existing systems work together. This integration is
not just about the physical setup; it's about ensuring the workflow, the
data exchange, and the human-machine interactions are optimized for the best
performance.
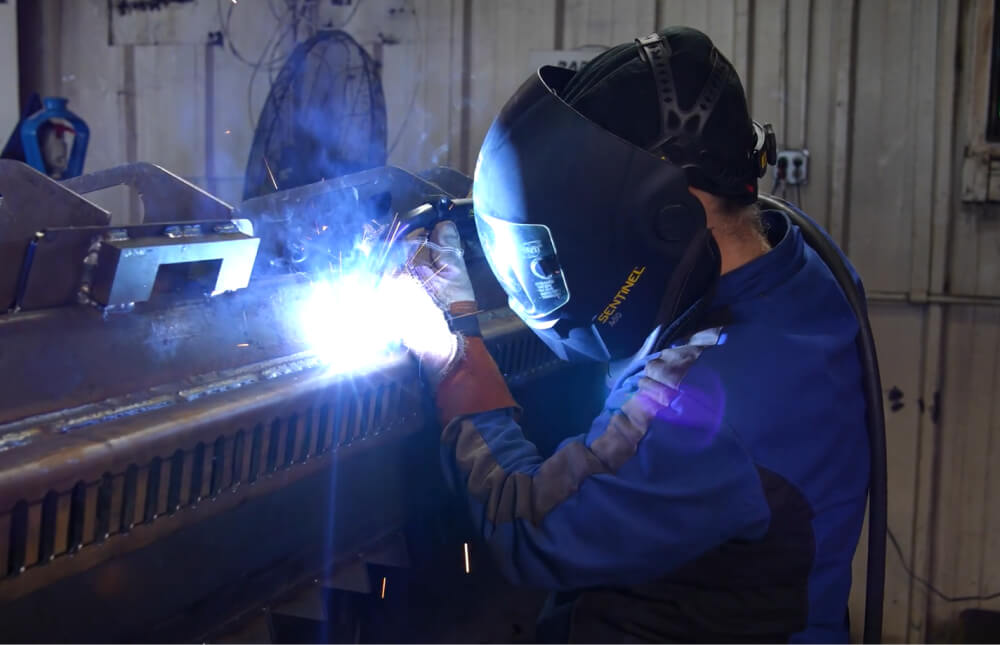

Comparative Analysis: Cobot Welding vs. Other Methods
Distinct Features of Different Welding Approaches
Welding methodologies vary significantly in their features and applications.
The primary categorization can be seen between manual welding, traditional
automated welding, and collaborative welding (cobot welding).
Manual Welding
In manual welding, a human welder performs the operations. The quality of
products relies heavily on their skills, ideal for small-scale operations or
detailed work requiring human touch and expertise. However, it could be
prone to common quality problems such as weld spatter, porosity, and shallow
penetration.
Traditional Automated Welding
Traditional automation in welding involves fully or semi-automated robotic
systems. In fully-automated robotic welding, robots guide the metal
throughout the process, while in semi-automated welding, a person loads and
unloads the metal. This method was initially ideal for large-scale
operations but has found a place in small and medium businesses due to its
benefits in productivity and quality.
Collaborative Welding (Cobot Welding)
Cobots, on the other hand, blend the best of both worlds. They work
alongside humans, enabling easy programming, quick adjustments, and
transitions between welding tasks. Cobots
are known for their flexibility, ease of programming, and lower
overall investment, making them a quick solution to address welder
shortages, and suitable for low-volume work.
Each welding method has its own advantages and disadvantages that must be
weighed against the specific needs and constraints of the welding task at
hand.
Traditional Automation vs. Collaborative Welding vs. Manual Welding
The welding industry has evolved over the years with the advent of
automation and collaborative robots (cobots). Each welding approach -
traditional automation, collaborative welding, and manual welding, has its
place in the industry based on certain factors, including the scale of
operations, the level of precision required, and the available resources.
Traditional Automation
Involves the use of robotic systems that are programmed to carry out welding
tasks autonomously. They are ideal for large-scale production where
high-speed and high-volume welding is required. The initial setup cost is
high, requiring a significant amount of space and specialized setup. They
offer high precision, consistency, and efficiency, reducing the likelihood
of errors and rework.
Collaborative Welding
Cobots are designed to work alongside human operators. They are easier to
program, set up, and they require less space compared to traditional robots.
Cobots are a more economical solution for small to medium-sized enterprises
or for operations where flexibility and easy reconfiguration are essential.
They offer a balance between automation and human intervention, allowing for
quick adjustments and transitions between different welding tasks. They can
be easily moved around and redeployed to different tasks or locations.
Manual Welding
Relies entirely on the skill and expertise of human welders. It is ideal for
specialized welding tasks, repair work, or small-scale operations. Manual
welding allows for a high level of customization and adaptability to
different tasks, but it is slower and may lack the consistency and precision
of automated systems.
The choice between these welding approaches depends largely on the specific
needs and constraints of the operation. While traditional automation may be
suitable for high-volume production, collaborative welding offers a flexible
and cost-effective solution for various applications. Manual welding, on the
other hand, remains indispensable for tasks requiring a high level of
craftsmanship and customization.
Each welding method: manual welding, traditional automated welding, and
collaborative welding, has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
These pros and cons can significantly influence the choice of welding method
for a particular application or industry.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Manual Welding
- Pros: High level of customization, adaptability to different tasks,
ideal for repair work or specialized welding tasks.
- Cons: Slower speed, inconsistency in weld quality, higher likelihood of
errors, and may require a higher level of skill and training.
Traditional Automated Welding
- Pros: High precision, consistency, and efficiency. Ideal for
high-volume production, reduces the likelihood of errors and rework and
can operate round the clock.
- Cons: High initial setup cost, requires significant space and
specialized setup, less flexible in adapting to different tasks or
changes in production.
Collaborative Welding (Cobot Welding)
- Pros: Ease of programming and setup, requires less space, more
economical for small to medium-sized enterprises. Offers a balance
between automation and human intervention, allowing for quick
adjustments and transitions between different welding tasks.
- Cons: May not be suitable for high-volume production compared to
traditional automated welding, may require a more controlled environment
to ensure safety, and may not offer the same level of precision as
traditional automated welding in complex tasks.
Understanding the pros and cons of each welding method can help
businesses
and industries make informed decisions based on their specific needs, budget
constraints, and the level of precision and consistency required in their
welding operations.
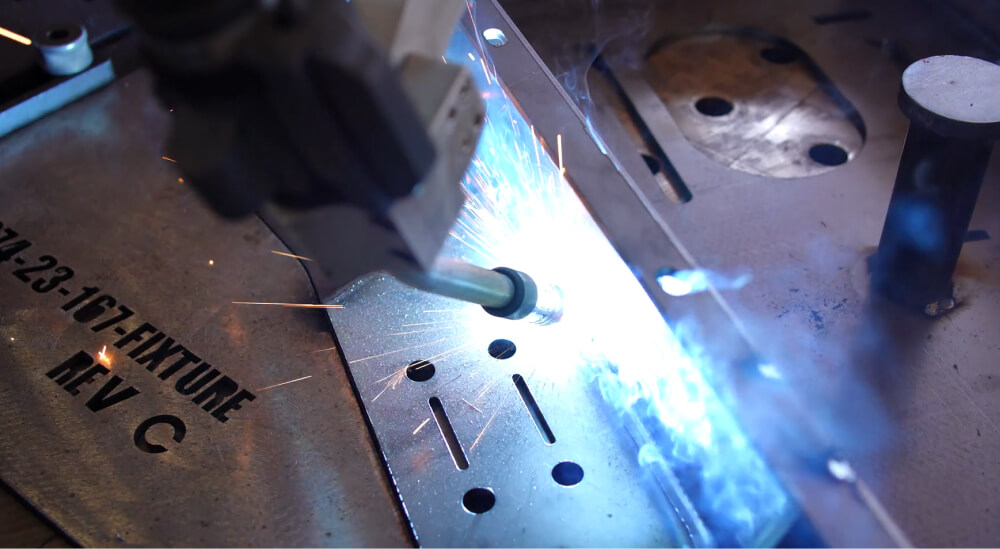
Challenges and Limitations
Skill and Training Requirements
Implementing welding cobots in a manufacturing setup necessitates a certain
level of skill and training for operators. Understanding the operating
procedures of welding cobots is crucial for ensuring efficiency and safety.
Welding cobots are designed with simplicity in mind, suitable for welders
new to robotic welding automation. A detailed step-by-step process is often
provided to guide operators on handling the cobot efficiently.
With the growing use of welding robots, the role of robotic welder welding
operators has become increasingly significant. They are responsible for
programming and operating welding robots to perform various tasks, including
MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
Operating a cobot requires some training but not extensive welding or
programming experience. This starkly contrasts traditional robotic welding
cells that demand more extensive welding or programming experience. Cobots
present a lower barrier to entry, making them an attractive option for
operations that struggle with skill shortages. Most suppliers offer training
to get staff comfortable with new equipment, ensuring a smooth transition to
utilizing cobots for welding tasks.
Limitations in Complex Tasks
While welding cobots bring many benefits to the table, they have limitations
when handling complex welding tasks. Their application can be constrained in
scenarios requiring intricate welding or tasks requiring high precision and
control. The accuracy of cobots might fall short in comparison to
traditional automated welding systems, especially in highly specialized or
complex welding applications.
Cobots may struggle with welding tasks that involve complicated geometries
or require multi-layer welding. They are designed for simpler, more
straightforward welding operations and may lack the advanced control systems
of traditional welding robots. Traditional automated welding systems might
still be preferred for complex or highly specialized welding tasks.
There's a limitation in the payload and the reach of cobots, which can be a
hurdle when dealing with large workpieces or extensive welding tasks. This
may necessitate using traditional robots for such demanding scenarios,
ensuring that the welding tasks are executed accurately and efficiently.
Maintenance and Durability Concerns
Much like traditional robots, welding cobots require regular maintenance to
ensure they function optimally over time. The maintenance routine usually
encompasses checking the robotic arm, the welding torch, and other integral
components for wear and tear. Overlooking maintenance can lead to decreased
performance, accuracy, and, potentially, the premature failure of the cobot.
Durability is another concern. The harsh conditions prevalent in welding
environments, such as high temperatures and the presence of metal spatter,
can take a toll on the lifespan of the cobot. This may necessitate frequent
replacements of certain parts or additional protective measures to safeguard
the cobot against the harsh welding environment.
Any malfunction or breakdown in the cobot system can lead to production
downtime, affecting the overall productivity and efficiency of the
manufacturing process. Therefore, having a robust maintenance schedule and
ensuring that the cobots are well-protected against harsh welding conditions
are crucial for realizing the long-term benefits of cobot welding.
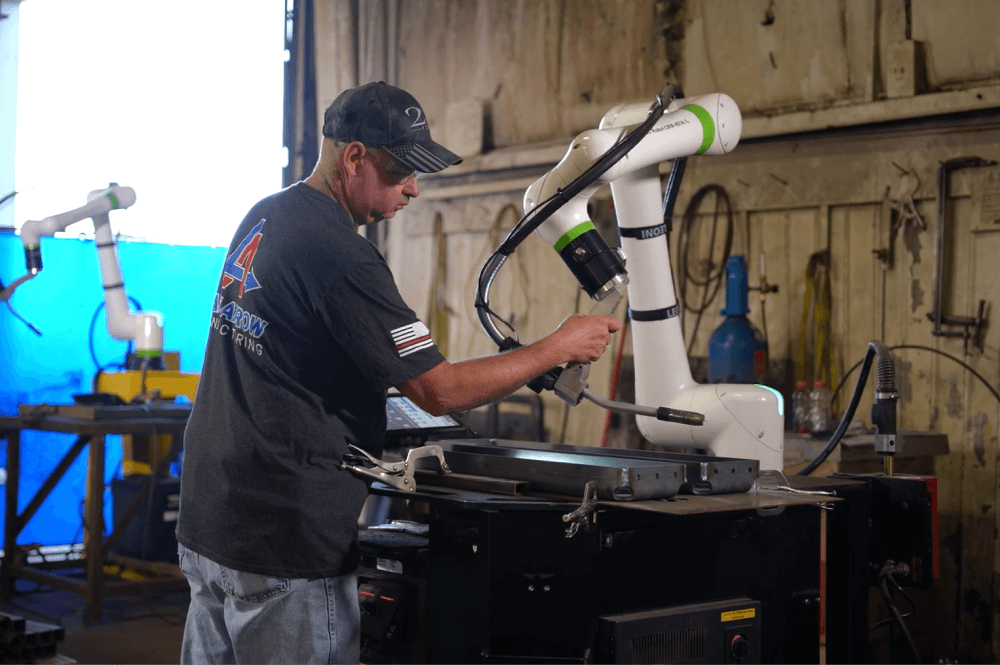
Human-Cobot Interaction in the Welding Industry
Role of Human Welders with Cobots
The advent of collaborative robots in the welding industry doesn’t
signify
the replacement of human welders. It denotes a shift in their roles within
the manufacturing environment. Cobots are designed to work alongside humans,
assisting in repetitive, strenuous, or hazardous tasks, allowing human
welders to focus on more complex, critical, or creative aspects of welding
tasks.
Human welders play a vital role in overseeing the operations carried out by
cobots, ensuring the quality of welds, and making necessary adjustments to
the cobot settings to achieve desired welding outcomes. They are
instrumental in programming the cobots, setting them up for different
welding tasks, and ensuring they operate safely and effectively.
Human welders can leverage the capabilities of cobots to increase their
productivity and efficiency. Cobots can handle the more monotonous or
dangerous aspects of welding, reducing the risk of occupational hazards for
human welders and freeing them up to tackle more challenging welding tasks
or focus on other important areas of the manufacturing process.
In essence, the collaboration between human welders and cobots facilitates a
synergistic relationship where both parties benefit. Human welders can
enhance their skill set by learning to operate and program cobots, while
cobots can augment the welding process by taking on more repetitive or
hazardous tasks. This collaboration aims to foster a safer, more productive,
and more satisfying work environment in the welding industry.
Training and Transitioning to Cobot Systems
Transitioning to cobot systems from manual or traditional automated welding
systems necessitates a certain level of training for the existing workforce.
Training programs are crucial for ensuring that operators and welders are
comfortable with the new technology and can utilize it to its full
potential. These programs typically cover the basics of operating the cobot,
programming it for various welding tasks, and troubleshooting common issues.
A significant advantage of cobots is their user-friendly interface and ease
of programming, which often allows for a smoother transition. This ease of
use reduces the learning curve significantly, enabling welders and operators
to quickly adapt to the new technology. Moreover, many cobot manufacturers
offer comprehensive training programs, both online and on-site, to help
facilitate this transition.
The transition also involves adapting the existing workflow and processes to
accommodate the new cobot systems. This may include reconfiguring the
workspace, setting up the cobots for the specific welding tasks, and
integrating them with other existing systems and machinery.
The transition to cobot systems can also open up opportunities for
upskilling the workforce. As welders and operators learn to work with and
program the cobots, they can acquire new skills that are valuable in the
modern manufacturing environment. Overall, with the right training and
support, transitioning to cobot systems can be a smooth process that
enhances the capabilities and skills of the existing workforce while
improving the efficiency and productivity of the welding operations.

Case Studies: Real-world Applications
Small-scale Manufacturing: Last Arrow Manufacturing
Small-scale manufacturers often grapple with the challenge of maintaining
cost-effectiveness while ensuring quality and flexibility in their
operations. Last Arrow Manufacturing, an Ohio-based contract manufacturer,
exemplified a successful transition towards automated welding while
retaining flexibility in their production processes.
The challenge was to automate simple, repetitive welding tasks without
compromising on quality, and at the same time, free up skilled welders for
more complex projects. The solution came in the form of FANUC's CRX welding
cobot, which provided the much-needed flexibility and ease of use.
Upon integrating FANUC’s welding cobots, Last Arrow Manufacturing
witnessed
a quick uptick in business, attributing to increased productivity, higher
profits, and improved employee satisfaction. The ease of programming was
highlighted by their Lead Programmer, Scott Musser, who with over 20 years
of experience in robotic programming, found the user-interface extremely
user-friendly.
Matt Bowling, the President of Last Arrow Manufacturing, expressed that the
integration of welding cobots provided a solution that works for their
business model, which requires consistent changeover due to the nature of
their projects. The case of Last Arrow Manufacturing illustrates the
potential of cobot integration in enhancing profitability, employee
satisfaction, and operational flexibility in small-scale manufacturing
setups, especially when dealing with frequent process changeovers and a
variety of welding tasks.
Investment Insights
In the manufacturing sector, the integration of cobots, particularly for
welding tasks, is viewed as a forward-thinking investment. This section
explores the reasoning behind investing in cobot welders, dives into a
comparative financial analysis between cobot and manual welding, and
discusses the return on investment along with the payback period
associated with such an investment.
Reasons to Invest in Cobot Welders
Investing in cobot welders comes with a plethora of benefits that
significantly contribute to a manufacturing facility’s bottom line.
- Ease of Use: Cobots are designed to be user-friendly, making it
possible for welders with beginner-level skills to operate them
efficiently. Their easy maneuverability and the straightforward process
of position or multipass welding make them a suitable choice for various
welding tasks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The initial investment in a welding cobot can
range from $50,000 to $100,000 or more. Although
this might seem steep, the long-term cost savings are substantial. The
automation of welding tasks leads to increased productivity, improved
quality, and reduced labor costs, presenting a cost-effective solution
in the long run.
- Market Growth: The cobot market is on a trajectory of rapid growth,
with an anticipated growth of 50% in 2023. This growth is propelled by
the looming welder shortage estimated at about 400,000 by 2024.
Investing in cobot welders not only addresses the labor shortage but
also positions a company to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving
market.
- Support and Accessibility: Post-sales support is crucial for ensuring
the smooth operation of cobot welders. Reputable cobot providers offer
accessible support, often in real-time over video calls, ensuring any
issues are resolved promptly, thus minimizing downtime.
- Addressing Labor Shortage: The severe labor shortage in the welding
sector is pushing manufacturers to seek automated solutions. Cobot
welders stand as a viable solution to this problem, helping maintain
production levels even in the face of dwindling interest in welding
careers among the younger generation.
Comparative Financial Analysis: Cobot vs. Manual Welding
In a financial analysis between cobot and manual welding, several aspects
come into play. The primary focus areas are the initial investment,
operational costs, productivity, and output quality.
The initial investment for setting up a cobot welding station might be higher
than that of a manual welding station due to the cost of the cobot and the
associated setup. However, this initial investment can be quickly offset by
the subsequent reduction in operational costs and increased productivity.
Operational costs in a manual welding setup are primarily driven by labor
costs, which include salaries, benefits, and training. In contrast, the
operational costs in a cobot welding setup are significantly lower
post-setup, with maintenance and energy being the primary ongoing costs.
Reducing labor costs is one of the most substantial financial benefits of
transitioning to cobot welding.
Productivity is another critical area where cobot welding shines. Cobots can
operate continuously without fatigue, leading to a substantial increase in
production output. They also ensure consistent quality, reducing the rate of
defective or sub-standard products, thus minimizing losses associated with
rework or scrap.
The output quality in cobot welding is often higher than manual welding,
especially for repetitive and straightforward tasks. Cobots provide precise
and consistent welding, which is crucial for meeting the stringent quality
standards in industries like automotive and aerospace.
In the long term, the financial benefits of investing in cobot welding
become evident. The reduction in operational costs, combined with increased
productivity and improved quality, contributes to a higher return on
investment, making cobot welding a financially sound choice for
manufacturers looking to modernize their operations and stay competitive in
the market.
Return on Investment and Payback Period
The Return on Investment (ROI) and payback period are crucial metrics for
manufacturers considering the integration of cobot welding into their
operations. These metrics provide a clear financial picture of the long-term
value and the time frame within which the initial investment can be
recovered.
The ROI is calculated by comparing the cost of investment to the monetary
benefits derived from the investment over a specific period. In the case of
cobot welding, the benefits include savings from reduced labor costs,
increased productivity, and improved quality which leads to lesser rework
and waste. The ROI for cobot welding can be significantly high, especially
in low-volume production environments with substantial cost savings and
productivity gains.
The payback period, however, is the time it takes for the savings and
benefits to equal the initial investment. Typically, the payback period for
cobot welding systems can range from a few months to a couple of years,
depending on the scale of operations and the cost of the cobot system. A
shorter payback period is often seen in scenarios where manual welding
operations are replaced in highly repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, thus
quickly realizing the cost-saving benefits of automation.
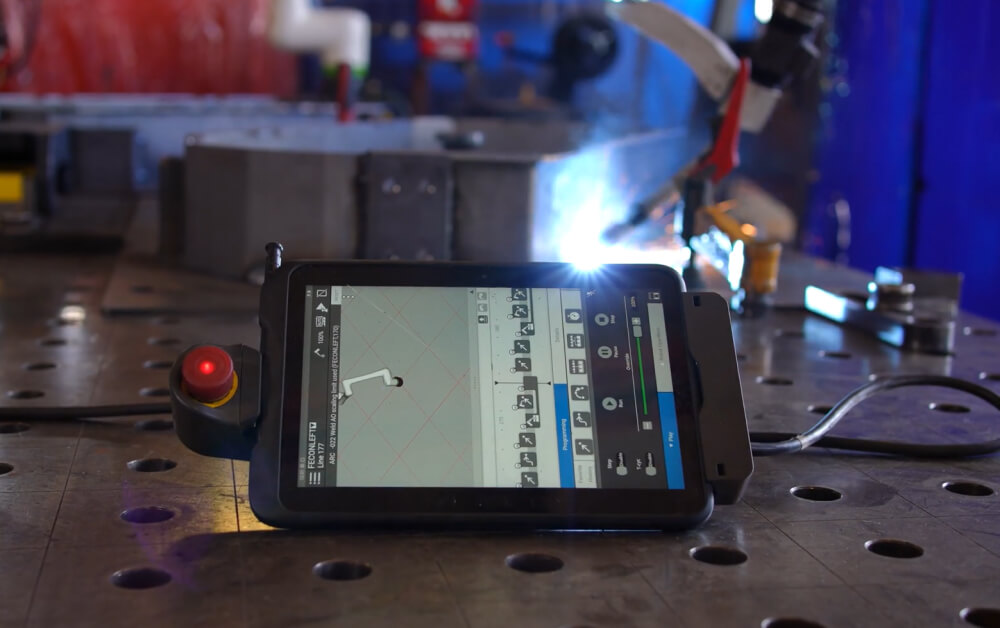
Technological Advancements on the Horizon
The future of cobot welding is intertwined with the continual advancements
in technology. These advancements aim at making cobot welding more
efficient, user-friendly, and adaptable to various manufacturing scenarios.
One notable trend is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
Machine Learning (ML) into cobot systems. This integration enables cobots to
learn from their environment and improve their performance over time. For
instance, they can learn to adjust their welding parameters autonomously to
account for variations in materials or environmental conditions, leading to
enhanced welding consistency and quality.
Advancements in sensor technology and vision systems are poised to
significantly improve the precision and capabilities of cobot welders.
Enhanced sensors and vision systems enable cobots to better understand their
environment, allowing for more accurate welding and improved error
detection.
Developing more sophisticated user interfaces and programming environments
is on the horizon. These advancements will make it easier for operators to
program and monitor cobot welders, reducing the barrier to entry and making
cobot welding accessible to a broader range of manufacturers.
Growth of the Cobot Market
The cobot market is expected to experience robust growth in the
coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing acceptance and
adoption of cobot welding in various manufacturing industry sectors. The
escalating demand for precision, consistency, and efficiency in welding
operations propels the need for cobot welding systems. Furthermore, the
looming labor shortages in the welding sector significantly contribute to
the growing interest in and adoption of cobot welding solutions.
Evolving Workplace Dynamics with Cobots
Integrating cobots in the welding sector is gradually altering the workplace
dynamics. Cobots are taking over repetitive and hazardous tasks, allowing
human welders to focus on more complex and creative aspects of welding
projects. This shift is fostering a more engaging and safer work
environment. Moreover, the ease of use and the low learning curve associated
with cobots encourage a more inclusive workforce, where individuals with
varying levels of technical expertise can contribute to welding projects.
This evolution is expected to continue as cobots become more advanced and
commonplace in the welding industry, promoting a harmonious collaboration
between human workers and robotic systems and ultimately leading to enhanced
productivity and job satisfaction among welding professionals.
Conclusion: The Role of Welding Cobots in Modern Manufacturing
The integration of welding cobots in modern manufacturing unveils a realm of
possibilities. Amidst the backdrop of labor shortages and the incessant
demand for high-quality products, cobot welding emerges as a viable
solution. Its adoption signals a step towards modernized manufacturing
processes characterized by increased efficiency, precision, and safety.
With their user-friendly interfaces, Cobots are demystifying robotics,
making it accessible to a broader spectrum of the workforce. This
inclusivity fosters a conducive environment for skill development and
knowledge transfer between human workers and robotic systems.
Moreover, the financial implications of integrating cobot welding are
profound. The initial investment is quickly offset by the substantial
reduction in operational costs and the notable increase in productivity.
Additionally, the competitive advantage gained through higher quality and
consistency in welding operations is invaluable.
Technological advancements foretell a future where cobots are integral to
manufacturing. They are poised to become more intelligent, adaptable, and
easier to operate, further solidifying their position in the manufacturing
landscape.
In summation, the role of welding cobots is pivotal in addressing modern
manufacturing challenges. They embody a significant stride towards creating
a more efficient, inclusive, and innovative manufacturing ecosystem, gearing
industries towards a future of enhanced productivity and global
competitiveness.
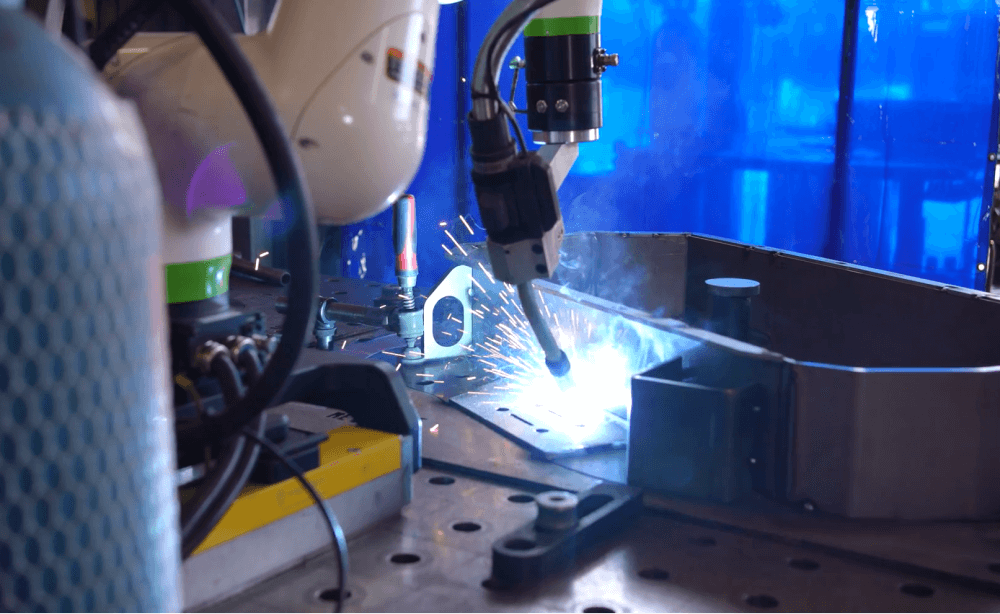
FANUC Welding Cobots
Explore a future of precision with FANUC Welding Cobots! Discover how our
cutting-edge cobot technology can revolutionize your welding operations,
ensuring impeccable quality, efficiency, and safety. Step into the future of
manufacturing with FANUC. Contact us today to learn more about our
innovative cobot welding solutions and how they can be tailored to meet your
production needs.
Key Takeaways
- Addressing Labor Shortages: The growing labor shortage in the welding
sector is a pressing issue, and cobot welding offers a viable solution
by automating routine tasks and maintaining production levels.
- Enhanced Precision and Safety: Cobots bring a new level of precision
to welding tasks, reducing errors and ensuring a safer work environment
by taking over hazardous tasks.
- Cost-Efficiency and ROI: Despite the initial investment, the long-term
cost savings, increased productivity, and potential for high return on
investment make cobot welding a financially sound choice.
- Ease of Integration: The user-friendly interfaces and ease of
programming make cobots an accessible technological upgrade, even for
small-scale manufacturers.
- Market Growth and Future Trends: The cobot market is on a trajectory
of rapid growth, propelled by technological advancements like AI
integration, improved sensor technology, and more sophisticated user
interfaces.
- Industry Applications: Real-world applications in various manufacturing
sectors illustrate the tangible benefits and successes of integrating
cobot welding into production processes.
- Evolving Workplace Dynamics: Cobots are fostering a more engaging,
inclusive, and safer work environment, promoting a harmonious
collaboration between human workers and robotic systems.
- Investment Insights: The analysis suggests a strong case for investing
in cobot welders, especially given the comparative financial benefits
over manual welding and the promising return on investment.
- Technological Advancements: The continual technological advancements
are set to further enhance the capabilities, efficiency, and
user-friendliness of cobot welding systems, solidifying their role in
modern manufacturing.