Straightness Compensation - FANUC CNC Technology
Machine tools that have long strokes can experience changes in straightness between their exes. This can affect machining accuracy. Using the Straightness Compensation feature, when an axis moves, the control calculates how much the other axes need to be compensated in order to maintain a straight path.
We'll help you find the best FANUC CNC technology and solutions to fit your needs.
Contact a FANUC CNC Systems Expert, today.
Contact us
In straightness compensation, similarly to Inclination compensation, four pitch error compensation points are selected from pitch error compensation points and specified as straightness compensation points. Compensation amounts are set up for these four points. For pitch error compensation points between straightness compensation points, the CNC calculates and outputs amounts that match straightness compensation. Straightness compensation largely differs from Inclination compensation in that the moving axis is not a compensation axis; Inclination compensation is applied directly to the moving axis. This relationship is specified by a parameter (for example, to apply compensation to the Y-axis as movement occurs along the X-axis).
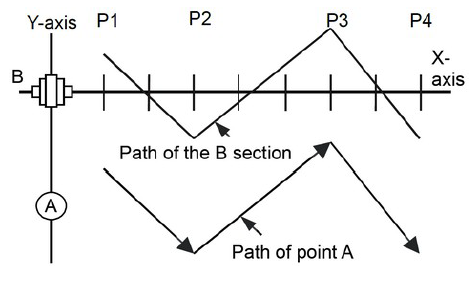
The straightness compensation function can be used after a moving axis and its compensation axis have returned to the reference position. To add the straightness compensation function option, the stored pitch error compensation option is needed. Straightness compensation data is superposed on stored pitch error compensation data and output. Straightness compensation is performed at pitch error compensation intervals. Straightness compensation does not allow the moving axis to be used as a compensation axis. To implement such compensation, use inclination compensation.
Benefits:
- Improved precision of perpendicular axes
- Improved machine precision
- Increased production quality and overall machine productivity